It is used to describe the area around an atomic nucleus where an electron will probably be. Describe Bohrs model of the atom.

Nucleus Of The Atom Ck 12 Foundation
To cancel out the positive charge of all of these protons more electrons were necessary.
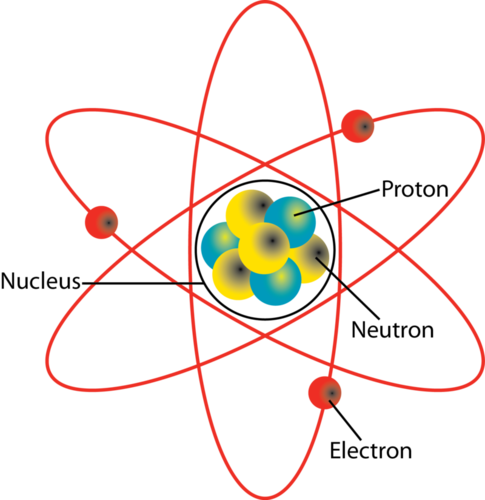
. The Bohr model shows that the electrons in atoms are in orbits of differing energy around the nucleus think of planets orbiting around the sun. So to overcome this and to explain the structure of atoms in detail Neil Bohr in 1912 proposed a model of atoms. Learn how atoms are made up of protons neutrons and electrons.
Only a limited number of orbits with certain energies are allowed. The nucleus of heavier atoms contains more protons than the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Classical physics cannot adequately describe all of the phenomena that occur at the atomic level.
The postulates of Bohrs model are given below. The electron in a hydrogen atom travels around the nucleus in a circular orbit. There are some drawbacks in Rutherfords atomic model.
The mass of an atom is determined by the total number of protons and neutrons. Elements are defined by the atomic number the number of protons in the nucleus. Activity will teach students about the combination of protons neutrons and electrons that make up every atom in the world.
The electrons in an atom are attracted to the protons in the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. The energy of the electron in an orbit is proportional to its distance from the nucleus. Niels Bohr a Danish scientist explained this line spectrum while developing a model for the atom.
It is the charge number of the nucleus since neutrons carry no net electrical charge. The atomic number of a chemical element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. Electromagnetic energy will be absorbed or emitted if.
An electron revolves around the nucleus in the orbit of an atom with fixed energy. The simplest example of the Bohr Model is for the hydrogen atom Z 1 or for a hydrogen-like ion Z 1 in which a negatively charged electron orbits a small positively charged nucleus. The atomic number determines the identity of an element and many of its chemical properties.
Bohr used the term energy levels or shells to. The further the electron is from the nucleus the more energy it has. Bohr Model for Heavier Atoms.
The modern periodic table is ordered by increasing atomic. Neutrons and protons commonly called nucleons are bound together in the dense inner core of an atom the nucleus where they account for 999 percent of the atoms mass. Electrons can escape from their orbit but only in response to an external source of energy being.
In other words the orbits are quantized.
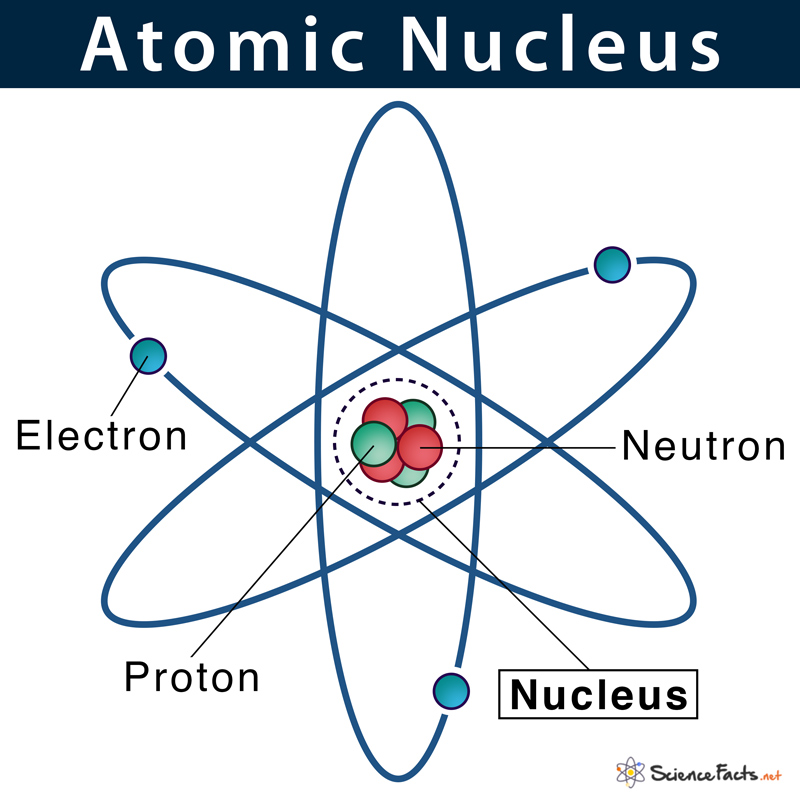
Atomic Nucleus Definition Structure Parts With Diagram
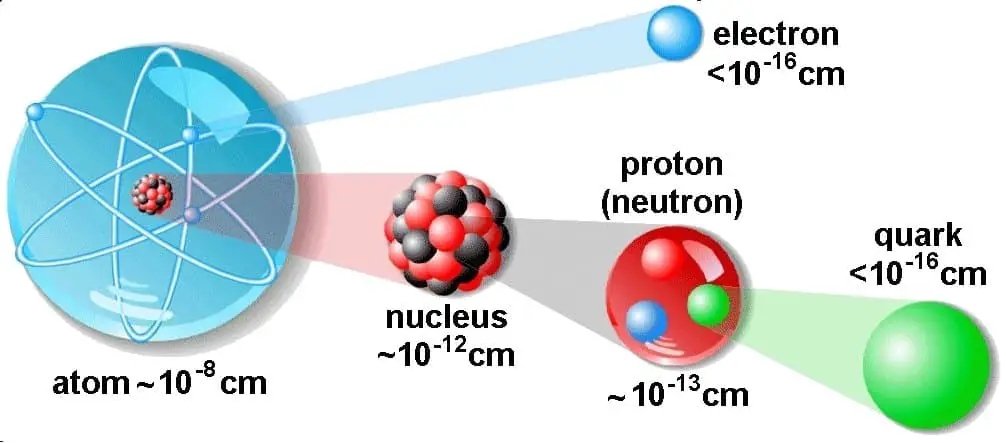
What Is Volume Of An Atom And Nucleus Definition

Does Every Atom Have A Nucleus Quora

What Two Particles Are Found In The Nucleus Of An Atom Socratic
0 Comments